A Complete Guide to Heraldry/Chapter 7
CHAPTER VII
THE FIELD OF A SHIELD AND THE HERALDIC TINCTURES
THE shield itself and its importance in armory is due to its being the vehicle whereon are elaborated the pictured emblems and designs which constitute coat-armour. It should be borne in mind that theoretically all shields are of equal value, saving that a shield of more ancient date is more estimable than one of recent origin, and the shield of the head of the house takes precedence of the same arms when differenced for a younger member of the family. A shield crowded with quarterings is interesting inasmuch as each quartering in the ordinary event means the representation through a female of some other family or branch thereof. But the real value of such a shield should be judged rather by the age of the single quartering which represents the strict male descent male upon male, and a simple coat of arms without quarterings may be a great deal more ancient and illustrious than a shield crowded with coat upon coat. A fictitious and far too great estimation is placed upon the right to display a long string of quarterings. In reality quarterings are no more than accidents, because they are only inherited when the wife happens to be an heiress in blood. It is quite conceivable that there may be families, in fact there are such families, who are able to begin their pedigrees at the time of the Conquest, and who have married a long succession of noble women, all of the highest birth, but yet none of whom have happened to be heiresses. Consequently the arms, though dating from the earliest period at which arms are known, would remain in their simple form without the addition of a solitary quartering. On the other hand, I have a case in mind of a marriage which took place some years ago. The husband is the son of an alien whose original position, if report speaks truly, was that of a pauper immigrant. His wealth and other attributes have placed him in a good social position; but he has no arms, and, as far as the world is aware, no ancestry whatever. Let us now consider his wife's family. Starting soon after the Conquest, its descendants obtained high position and married heiress after heiress, and before the commencement of this century had amassed a shield of quarterings which can readily be proved to be little short of a hundred in number. Probably the number is really much greater. A large family followed in one generation, and one of the younger sons is the ancestor of the aforesaid wife. But the father of this lady never had any sons, and though there are many males of the name to carry on the family in the senior line and also in several younger branches, the wife, by the absence of brothers, happens to be a coheir; and as such she transmits to her issue the right to all the quarterings she has inherited. If the husband ever obtains a grant of arms, the date of them will be subsequent to the present time; but supposing such a grant to be obtained, the children will inevitably inherit the scores of quarterings which belong to their mother. Now it would be ridiculous to suppose that such a shield is better or such a descent more enviable than the shield of a family such as I first described. Quarterings are all very well in their way, but their glorification has been carried too far.
A shield which displays an augmentation is of necessity more honourable than one without. At the same time no scale of precedence has ever been laid down below the rank of esquires; and if such precedence does really exist at all, it can only be according to the date of the grant. Here in England the possession of arms carries with it no style or title, and nothing in his designation can differentiate the position of Mr. Scrope of Danby, the male descendant of one of the oldest families in this country, whose arms were upheld in the Scrope and Grosvenor controversy in 1390, or Mr. Daubeney of Cote, from a Mr. Smith, whose known history may have commenced at the Foundling Hospital twenty years ago. In this respect English usage stands apart, for whilst a German is "Von" and a Frenchman was "De," if of noble birth, there is no such apparent distinction in England, and never has been. The result has been that the technical nobility attaching to the possession of arms is overlooked in this country. On the Continent it is usual for a patent creating a title to contain a grant of the arms, because it is recognised that the two are inseparable. This is not now the case in England, where the grant of arms is one thing and the grant of the title another, and where it is possible, as in the case of Lord St. Leonards, to possess a peerage without ever having obtained the first step in rank, which is nobility or gentility.
The foregoing is in explanation of the fact that except in the matter of date all shields are equal in value.
So much being understood, it is possible to put that consideration on one side, and speaking from the artistically technical point of view, the remark one often hears becomes correct, that the simpler a coat of arms the better. The remark has added truth from the fact that most ancient coats of arms were simple, and many modern coats are far from being worthy of such a description.
A coat of arms must consist of at least one thing, to wit, the "field." This is equivalent in ordinary words to the colour of the ground of the shield. A great many writers have asserted that every coat of arms must consist of at least the field, and a charge, though most have mentioned as a solitary exception the arms of Brittany, which were simply "ermine." A plain shield of ermine (Fig. 33) was borne by John of Brittany, Earl of Richmond (d. 1399), though some of his predecessors had relegated the arms of Brittany to a "quarter ermine" upon more elaborate escutcheons (Fig. 61). This idea as to arms of one tincture was, however, exploded in Woodward and Burnett's "Treatise on Heraldry," where no less than forty different examples are quoted. The above-mentioned writer continues: "There is another use of a plain red shield which must not be omitted. In the full quartered coat of some high sovereign princes of Germany—Saxony (duchies), Brandenburg (Prussia), Bavaria, Anhalt—appears a plain red quartering; this is known as the Blut Fahne or Regalien quarter, and is indicative of Royal prerogatives. It usually occupies the base of the shield, and is often diapered."

Fig. 33.—Arms of John (de Montfort, otherwise de Bretagne), Duke of Brittany and Earl of Richmond. (From his seal.)
But in spite of the lengthy list which is quoted in Woodward and Burnett, the fact remains that only one British instance is included. The family of Berington of Chester (on the authority of Harleian manuscript No. 1535) is said to bear a plain shield of azure. Personally I doubt this coat of arms for the Berington family of Chester, which is probably connected with the neighbouring family in Shropshire, who in later times certainly used very different arms. The plain shield of ermine is sometimes to be found as a quartering for Brittany in the achievement of those English families who have the right to quarter the Royal arms; but I know of no other British case in which, either as a quartering or as a pronominal coat, arms of one tincture exist.
But there are many coats which have no charge, the distinctive device consisting of the partition of the shield in some recognised heraldic method into two or more divisions of different tinctures. Amongst such coats may be mentioned the arms of Waldegrave, which are simply: Party per pale argent and gules; Drummond of Megginch, whose arms are simply: Party per fess wavy or and gules; and the arms of Boyle, which are: Per bend embattled argent and gules. The arms of Berners—which are: Quarterly or and vert—are another example, as are the arms of Campbell (the first quarter in the Duke of Argyll's achievement), which are: Gyronny or and sable.
The coat bendy argent and gules, the ancient arms of Talbot, which are still borne as a quartering by the Earl of Shrewsbury, Waterford, and Talbot; and the coat chequy or and azure, a quartering for Warren, which is still borne by the House of Howard, all come within the same category. There are many other coats of this character which have no actual charge upon them.
The colour of the shield is termed the field when it consists of only one colour, and when it consists of more than one colour the two together compose the field. The field is usually of one or more of the recognised metals, colours, or furs.
The metals are gold and silver, these being termed "or" and "argent." The colours, which are really the "tinctures," if this word is to be used correctly, are: gules (red), azure (blue), vert (green), purpure (purple), and (in spite of the fact that it is not really a colour) black, which is known as sable.
The metal gold, otherwise "or," is often represented in emblazonments by yellow: as a matter of fact yellow has always been used for gold in the Register Books of the College of Arms, and Lyon Office has recently reverted to this practice. In ancient paintings and emblazonments the use of yellow was rather more frequent than the use of gold, but gold at all times had its use, and was never discarded. Gold seems to have been usually used upon ancient patents, whilst yellow was used in the registrations of them retained in the Offices of Arms, but I know of no instance in British armory in which the word yellow has been used in a blazon to represent any tint distinct from gold. With regard to the other metal, silver, or, as it is always termed, "argent," the same variation is found in the usage of silver and white in representing argent that we find in yellow and gold, though we find that the use of the actual metal (silver) in emblazonment does not occur to anything like the same extent as does the use of gold. Probably this is due to the practical difficulty that no one has yet discovered a silver medium which does not lose its colour. The use of aluminium was thought to have solved the difficulty, but even this loses its brilliancy, and probably its usage will never be universally adopted. This is a pity, for the use of gold in emblazonments gives a brilliancy in effect to a collection of coat-armour which it is a pity cannot be extended by an equivalent usage of silver. The use of silver upon the patents at the College of Arms has been discontinued some centuries, though aluminium is still in use in Lyon Office. Argent is therefore usually represented either by leaving the surface untouched, or by the use of Chinese white.
I believe I am the first heraldic writer to assert the existence of the heraldic colour of white in addition to the heraldic argent. Years ago I came across the statement that a white label belonged only to the Royal Family, and could be used by no one else. I am sorry to say that though I have searched high and low I cannot find the authority for the statement, nor can I learn from any officer of arms that the existence of such a rule is asserted; but there is this curious confirmation that in the warrants by which the various labels are assigned to the different members of the Royal Family, the labels are called white labels. Now the label of the Prince of Wales is of three points and is plain. Heraldry knows nothing of the black lines which in drawing a coat of arms usually appear for the outline of a charge. In older work such lines are absent. In any case they are only mere accidents of draughtsmanship. Bearing this in mind, and bearing in mind that the sinister supporter of the Prince of Wales is a unicorn argent, how on earth is a plain label of argent to be depicted thereupon? Now it is necessary also that the label shall be placed upon the crest, which is a lion statant guardant or, crowned with the coronet of the Prince, and upon the dexter supporter which is another golden lion; to place an argent label upon either is a flat violation of the rule which requires that metal shall not be placed upon metal, nor colour upon colour; but if the unicorn is considered argent, which it is, it would if really depicted in silver be quite possible to paint a white label upon it, for the distinction between white and silver is marked, and a white label upon a gold lion is not metal upon metal. Quite recently a still further and startling confirmation has come under my notice. In the grant of a crest to Thomas Mowbray, Earl of Nottingham, the coronet which is to encircle the neck of the leopard is distinctly blazoned argent, the label to which he is previously said to have had a just hereditary right is as distinctly blazoned white, and the whole grant is so short that inadvertence could hardly be pleaded as an explanation for the distinction in blazon. Instances of an official exemplification of coats of arms with labels are not uncommon, because the label in some number of families, for example Courtenay and Prideaux-Brune and Barrington, has become stereotyped into a charge. In none of these cases, however, is it either argent or white, but instances of the exemplification of a coat of arms bearing a label as a mark of cadency are, outside the members of the Royal Family, distinctly rare; they are necessarily so, because outside the Royal Family the label is merely the temporary mark of the eldest son or grandson during the lifetime of the head of the house, and the necessity for the exemplification of the arms of an eldest son can seldom occur. The one circumstance which might provide us with the opportunity is the exemplification consequent upon a change of name and arms by an eldest son during the lifetime of his father; but this very circumstance fails to provide it, because the exemplification only follows a change of arms, and the arms being changed, there no longer exists the necessity for a mark of cadency; so that instances of the official use of a label for cadency are rare, but of such as occur I can learn of none which has received official sanction which blazons the label white. There is, however, one coat which is said to have a label argent as a charge, this is the coat of Fitz-Simon, which is quoted in Papworth, upon the authority of one of the Harleian Manuscripts, as follows: Sable, three crescents, in chief a label of two drops and in fess another of one drop argent; and the same coat of arms is recorded in a funeral entry in Ulster's Office. The label is not here termed white, and it is peculiar that we find it of another colour in another coat of Fitz-Simon (azure, a lion rampant ermine, a label of four point gules).

Fig. 34.—Armorial bearings of Henry de Lacy, Earl of Lincoln (d. 1311): Or, a lion rampant purpure. (From his seal.)
Of other colours may be mentioned purpure (purple). This in English heraldry is a perfectly well recognised colour, and though its use is extremely rare in comparison with the others, it will be found too frequently for it to be classed as an exception. The earliest instance of this tincture which I have met with is in the coat of De Lacy (Fig. 34). The Roll of Caerlaverock speaks of his
- "Baniere ot de un cendall saffrin,
- O un lion rampant porprin,"
whilst MS. Cott. Calig. A. xviii. quotes the arms: "De or, a un lion rampaund de pourpre." The Burton coat of the well-known Shropshire family of Lingen-Burton is: Quarterly purpure and azure, a cross engrailed or between four roses argent. The Irish baronets of the name of Burton, who claimed descent from this family, bore a very similar coat, namely: Per pale azure and purpure, a cross engrailed or between four roses argent.
Two other colours will be found in nearly all text-books of English armory. These are murrey or sanguine, and orange or tenné. The exact tint of murrey is between gules and purpure; and tenné is an orange-tawny colour. They are both "stains," and were perhaps invented by the old heralds for the perpetration of their preposterous system of abatements, which will be found set out in full in the old heraldry books, but which have yet to be found occurring in fact. The subject of abatements is one of those pleasant little insanities which have done so much to the detriment of heraldry. One, and one only, can be said to have had the slightest foundation in fact; that was the entire reversal of the escutcheon in the ceremony of degradation following upon attainder for high treason. Even this, however, was but temporary, for a man forfeited his arms entirely by attainder. They were torn down from his banner of knighthood; they were erased in the records of the College of Arms; but on that one single occasion when he was drawn upon a hurdle to the place of his execution, they are said to have been painted reversed upon paper, which paper was fastened to his breast. But the arms then came to an end, and his descendants possessed none at all. They certainly had not the right to depict their shield upside down (even if they had cared to display such a monstrosity). Unless and until the attainder was reversed, arms (like a title) were void; and the proof of this is to be found in the many regrants of arms made in cases where the attainder has remained, as in the instances of the Earl of Stafford and the ancestor of the present Lord Barnard. But that any person should have been supposed to have been willing to make use of arms carrying an abatement is preposterous, and no instance of such usage is known. Rather would a man decline to bear arms at all; and that any one should have imagined the existence of a person willing to advertise himself as a drunkard or an adulterer, with variations in the latter case according to the personality of his partner in guilt, is idiotic in the extreme. Consequently, as no example of an abatement has ever been found, one might almost discard the "stains" of murrey and tenné were it not that they were largely made use of for the purposes of liveries, in which usage they had no such objectionable meaning. At the present day scarlet or gules being appropriated to the Royal Family for livery purposes, other people possessing a shield of gules are required to make use of a different red, and though it is now termed chocolate or claret colour by the utilitarian language of the day, it is in reality nothing more than the old sanguine or murrey. Of orange-tawny I can learn of but one livery at the present day. I refer to the orange-tawny coats used by the hunt servants of Lord Fitzhardinge, and now worn by the hunt servants of the Old Berkeley country, near London. A propos of this it is interesting to note the curious legend that the "pink" of the hunting field is not due to any reasons of optical advantage, but to an entirely different reason. Formerly no man might hunt even on his own estate until he had had licence of free warren from the Crown. Consequently he merely hunted by the pleasure of the Crown, taking part in what was exclusively a Royal sport by Royal permission, and for this Royal sport he wore the King's livery of scarlet. This being the case, it is a curious anomaly that although the livery of the only Royal pack recently in existence, the Royal Buck Hounds, was scarlet and gold, the Master wore a green coat. The legend may be a fallacy, inasmuch as scarlet did not become the Royal livery until the accession of the Stuarts; but it is by no means clear to what date the scarlet hunting coat can be traced.
There is, however, one undoubted instance of the use of sanguine for the field of a coat of arms, namely, the arms of Clayhills of Invergowrie,[1] which are properly matriculated in Lyon Register.
To these colours German heraldry has added brown, blood-red (this apparently is different from the English sanguine, as a different hatching has been invented for it), earth-colour, iron-grey, water-colour, flesh-colour, ashen-grey, orange (here also a separate hatching from the one to represent tenné has been invented), and the colour of nature, i.e. "proper." These doubtless are not intended to be added to the list of heraldic tinctures, but are noted because various hatchings have been invented in modern times to represent them.
Mr. Woodward, in Woodward and Burnett's "Treatise on Heraldry," alludes to various tinctures amongst Continental arms which he has come across.
"Besides the metals, tinctures, and furs which have been already described, other tinctures are occasionally found in the Heraldry of Continental nations; but are comparatively of such rarity as that they may be counted among the curiosities of blazon, which would require a separate volume. That of which I have collected instances is Cendrée, or ash colour, which is borne by (among others) the Bavarian family of Ashua, as its armes parlantes: Cendrée, a mount of three coupeaux in base or.
"Brunâtre, a brown colour, is even more rare as a tincture of the field; the Mieroszewsky in Silesia bear, 'de Brunâtre, A cross patée argent supporting a raven rising sable, and holding in its beak a horseshoe proper, its points towards the chief."
"Bleu-céleste, or bleu du ciel, appears occasionally, apart from what we may term 'landscape coats.' That it differs from, and is a much lighter colour than, azure is shown by the following example. The Florentine Cinti (now Cini) bear a coat which would be numbered among the armes fausses, or à enquérir: Per pale azure and bleu-céleste, an estoile counterchanged."
"Amaranth or columbine is the field of a coat (of which the blazon is too lengthy for insertion in this place) which was granted to a Bohemian knight in 1701."
Carnation is the French term for the colour of naked flesh, and is often employed in the blazonry of that country.
Perhaps mention should here be made of the English term "proper." Anything, alive or otherwise, which is depicted in its natural colours is termed "proper," and it should be depicted in its really correct tones or tints, without any attempt to assimilate these with any heraldic tincture. It will not be found in the very ancient coats of arms, and its use is not to be encouraged. When a natural animal is found existing in various colours it is usual to so describe it, for the term "proper" alone would leave uncertainty. For instance, the crest of the Lane family, which was granted to commemorate the ride of King Charles II. behind Mistress Jane Lane as her servant, in his perilous escape to the coast after the disastrous Battle of Worcester, is blazoned "a strawberry roan horse, couped at the flanks proper, bridled sable, and holding between the feet an Imperial crown also proper." Lord Cowper's supporters were, on either side of the escutcheon, "a light dun horse proper, with a large blaze down the face, the mane close shorn except a tuft on the withers, a black list down the back, a bob tail, and the near fore-foot and both hind feet white." Another instance that might be quoted are the supporters of Lord Newlands, which are: "On either side a dapple-grey horse proper, gorged with a riband and suspended therefrom an escutcheon gules, charged with three bezants in chevron." The crest of the family of Bewes, of St. Neots, Cornwall, is: "On a chapeau gules, turned up ermine, a pegasus rearing on his hind legs of a bay colour, the mane and tail sable, winged or, and holding in the mouth a sprig of laurel proper."
There are and were always many occasions in which it was desired to represent armorial bearings in black and white, or where from the nature of the handicraft it was impossible to make use of actual colour. But it should always be pointedly remembered that unless the right colours of the arms could be used the tinctures were entirely ignored in all matters of handicraft until the seventeenth century. Various schemes of hatchings, however, were adopted for the purpose of indicating the real heraldic colours when arms were represented and the real colours could not be employed, the earliest being that of Francquart in Belgium, circa 1623. Woodward says this was succeeded by the systems of Butkens, 1626; Petra Sancta, 1638; Lobkowitz, 1639; Gelenius; and De Rouck, 1645; but all these systems differed from each other, and were for a time the cause of confusion and not of order. Eventually, however, the system of Petra Sancta (the author of Tesseræ Gentilitia) superseded all the others, and has remained in use up to the present time.

Fig. 35.
Upon this point Herr Ströhl in his Heraldischer Atlas remarks: "The system of hatching used by Marcus Vulson de la Colombière, 1639, in the course of time found acceptance everywhere, and has maintained itself in use unaltered until the present day, and these are shown in Fig. 35, only that later, hatchings have been invented for brown, grey, &c.; which, however, seems rather a superfluous enriching." None of these later creations, by the way, have ever been used in this country. For the sake of completeness, however, let them be mentioned (see Fig. 36): a, brown; b, blood-red; c, earth-colour; d, iron-grey; e, water-colour; f, flesh-colour; g, ashen-grey; h, orange; and i, colour of nature. In English armory "tenné" is represented by a combination of horizontal (as azure) lines with diagonal lines from sinister to dexter (as purpure), and sanguine or murrey by a combination of diagonal lines from dexter to sinister (as vert), and from sinister to dexter (as purpure).

Fig. 36.
The hatchings of the shield and its charges always accommodate themselves to the angle at which the shield is placed, those of the crest to the angle of the helmet. A curious difficulty, however, occurs when a shield, as is so often the case in this country, forms a part of the crest. Such a shield is seldom depicted quite upright upon the wreath. Are the tincture lines to follow the angle of the smaller shield in the crest or the angle of the helmet? Opinion is by no means agreed upon the point.
But though this system of representing colours by "hatching" has been adopted and extensively made use of, it is questionable whether it has ever received official sanction, at any rate in Great Britain. It certainly has never been made use of in any official record or document in the College of Arms. Most of the records are in colour. The remainder are all without exception "tricked," that is, drawn in outline, the colours being added in writing in the following contracted forms: "O," or "or," for or; "A," "ar," or "arg," for argent; "G," or "gu," for gules; "Az," or "B" (for blue, owing to the likelihood of confusion between "ar" and "az," "B" being almost universally used in old trickings), for azure; "S," or "sa," for sable; "Vt" for vert, and "Purp" for purpure. It is unlikely that any change will be made in the future, for the use of tincture lines is now very rapidly being discarded by all good heraldic artists in this country. With the reversion to older and better forms and methods these hatchings become an anachronism, and save that sable is represented by solid black they will probably be unused and forgotten before very long.
The plain, simple names of colours, such as red and green, seemed so unpoetical and unostentatious to the heralds and poets of the Middle Ages, that they substituted for gold, topaz; for silver, pearl or "meergries"; for red, ruby; for blue, sapphire; for green, emerald; and for black, diamond or "zobel" (sable, the animal, whence the word "sable"). Let the following blazonment from the grant of arms to Mödling bei Wien in 1458 serve as example of the same: "Mit namen ain Schilt gleich getailt in fasse, des ober und maister tail von Rubin auch mit ainer fasse von Berlein, der under thail von grunt des Schilts von Schmaragaden, darinneain Pantel von Silber in Rampannt"—(lit. "Namely, a shield equally divided in fess, the upper and greater part of ruby, also with a fess of pearl, the under part of the field of the shield of emerald, therein a panther of silver, rampant"); that is, "Per fess gules and vert, in chief a fess argent, in base a panther rampant of the last."
Even the planets, and, as abbreviations, their astronomical signs, are occasionally employed: thus, the sun for gold, the moon for silver, Mars for red, Jupiter for blue, Venus for green, Saturn for black, and Mercury for purple. This aberration of intellect on the part of mediæval heraldic writers, for it really amounted to little more, had very little, if indeed it had any, English official recognition. No one dreams of using such blazon at the present time, and it might have been entirely disregarded were it not that Guillim sanctions its use; and he being the high priest of English armory to so many, his example has given the system a certain currency. I am not myself aware of any instance of the use of these terms in an English patent of arms.
The furs known to heraldry are now many, but originally they were only two, "ermine" and "vair." Ermine, as every one knows, is of white covered with black spots, intended to represent the tails of the animal. From ermine has been evolved the following variations, viz. ermines, erminois, pean, and erminites. "Ermines" is a black field with white ermine spots (the French term for this is contre-hermin, the German, gegen-hermelin). A gold background with black ermine spots is styled erminois, and pean is a black ground with gold ermine spots. Planché mentions still another, as does Parker in his "Glossary of Heraldry," namely, "erminites," which is supposed to be white, with black ermine spots and a red hair on each side of the spot. I believe there is no instance known of any such fur in British armory. It is not mentioned in Ströhl's "Heraldic Atlas," nor can I find any foreign instance, so that who invented it, or for what purpose it was invented, I cannot say; and I think it should be relegated, with abatements and the seize quartiers of Jesus Christ, to the category of the silly inventions of former heraldic writers, not of former heralds, for I know of no official act which has recognised the existence of erminites. The German term for erminois is gold-hermelin, but there are no distinctive terms either in French or German heraldry for the other varieties. Thus, erminois would be in French blazon: d'or, semé d'hermines de sable; pean would be de sable, semé d'hermines d'or. Though ermine is always nowadays represented upon a white background, it was sometimes depicted with black ermine spots upon a field of silver, as in the case of some of the stall plates of the Knights of the Garter in St. George's Chapel at Windsor. Ermine spots are frequently to be found as charges. For instance, in the well-known coat of Kay, which is: "Argent, three ermine spots in bend between two bendlets sable, the whole between as many crescents azure." As charges two ermine spots figure upon the arms recently granted to Sir Francis Laking, Bart., G.C.V.O. The ermine spot has also sometimes been used in British armory as the difference mark granted under a Royal Licence to assume name and arms when it is necessary to indicate the absence of blood relationship. Other instances of the use of an ermine spot as a charge are:—
Or, on two bars azure, as many barrulets dancetté argent, a chief indented of the second charged with an ermine spot or (Sawbridge).
Argent, a chevron between three crows sable, in each beak an ermine spot (Lloyd, Bishop of St. Asaph, 1680; Lichfield, 1692; and Worcester, 1700-17).
Argent, a fess gules between three ermine spots sable (Kilvington).
Argent, two bars sable, spotted ermine, in chief a lion passant gules (Hill, co. Wexford).
The earliest form in which ermine was depicted shows a nearer approach to the reality of the black tail, inasmuch as the spots above the tail to which we are now accustomed are a modern variant.
When a bend is ermine, the spots (like all other charges placed upon a bend) must be bendwise; but on a chevron, saltire, &c., they are drawn upright.
The other variety of fur is "vair." This originated from the fur of a kind of squirrel (the ver or vair, differently spelt; Latin varus), which was much used for the lining of cloaks. The animal was bluey-grey upon the back and white underneath, and the whole skin was used. It will be readily seen that by sewing a number of these skins together a result is obtained of a series of cup-shaped figures, alternating bluey-grey and white, and this is well shown in Fig. 28, which shows the effigy upon the tomb of Geoffrey Plantagenet, Count of Anjou, where the lining of vair to his cloak is plainly to be seen.

Fig. 37.—Arms of William de Ferrers, Earl of Derby (d. 1247): "Scutum variatum auro & gul." (From MS. Cott. Nero, D. 1.)
The word seems to have been used independently of heraldry for fur, and the following curious error, which is pointed out in Parker's "Glossary of the Terms used in Heraldry," may be noted in passing. The familiar fairy tale of Cinderella was brought to us from the French, and the slippers made of this costly fur, written, probably, verre for vairé, were erroneously translated "glass" slippers. This was, of course, an impossible material, but the error has always been repeated in the nursery tale-books.

Fig. 38.—Arms of Robert de Ferrers, Earl of Derby (1254-1265). (From stained glass in Dorchester Church.)
In the oldest records vair is represented by means of straight horizontal lines alternating with horizontal wavy or nebuly lines (see Fig. 37), but the cup-shaped divisions therefrom resulting having passed through various intermediate forms (see Fig. 38), have now been stereotyped into a fixed geometrical pattern, formed of rows of ear-shaped shields of alternate colours and alternately reversed, so depicted that each reversed shield fits into the space left by those on either side which are not reversed (see Fig. 39, k). The accompanying illustration will show plainly what is intended. In some of the older designs it was similar to that shown in the arms of the Earl Ferrers, Earl of Derby, 1254-65, the sketch (Fig. 38) being taken from almost contemporary stained glass in Dorchester Church, Oxon.; whilst sometimes the division lines are drawn, after the same manner, as nebuly. There does not seem to have been any fixed proportion for the number of rows of vair, as Fig. 40 shows the arms of the same Earl as represented upon his seal. The palpable pun upon the name which a shield vairé supplied
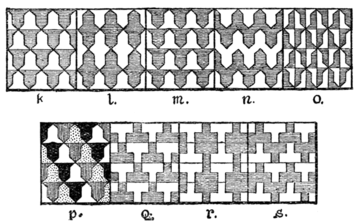
Fig. 39.
no doubt affords the origin of the arms of Ferrers. Some families of the name at a later date adopted the horseshoes, which are to be found upon many Farrer and Ferrers shields, the popular assumption being that they are a reference to the "farrier" from whom some would derive the surname. Woodward, however, states that a horseshoe being the badge of the Marshalls, horseshoes were assumed as armes parlantes by their descendants the Ferrers, who appear to have borne: Sable, six horseshoes argent. As a matter of fact the only one of that family who bore the horseshoes seems to have been William de Ferrers, Earl of Derby (d. 1254), as will be seen from the arms as on his seal (Fig. 41). His wife was Sybilla, daughter of William Marshall, Earl of Pembroke. His son reverted to the plain shield of vairé, or, and gules. The arms of the Ferrers family at a later date are found to be: Gules, seven mascles conjoined or, in which form they are still borne by Ferrers of Baddesley Clinton; but whether the mascles are corruptions of the horseshoes, or whether (as seems infinitely more probable) they are merely a corrupted form of the vairé, or, and gules, it is difficult to say. Personally I rather doubt whether any Ferrers ever used the arms: Argent, six horseshoes sable.
The early manner of depicting vair is still occasionally met with in foreign heraldry, where it is blazoned as Vair ondé or Vair ancien. The family of Margens in Spain bears: Vair ondé, on a bend gules three griffins or; and Tarragone of Spain: Vair ondé, or and gules. German heraldry seems to distinguish between wolkenfeh (cloud vair) and wogenfeh (wave vair; see Fig. 39, n). The former is equivalent to vair ancient, the latter to vair en point.
The verbal blazon of vair nearly always commences with the metal, but in the arrangement of the panes there is a difference between French and English usage. In the former the white panes are generally (and one thinks more correctly) represented as forming the first, or upper, line; in British heraldry the reverse is more usually the case. It is usual to depict the white panes of ordinary vair with white rather than silver, though the use of the latter cannot be said to be incorrect, there being precedents in favour of that form. When an ordinary is of vair or vairy, the rows of vair may be depicted either horizontally or following the direction of the ordinary. There are accepted precedents for both methods.
Vair is always blue and white, but the same subdivision of the field is frequently found in other colours; and when this is the case, it is termed vairy of such and such colours. When it is vairy, it is usually of a colour and metal, as in the case of Ferrers, Earls of Derby, above referred to; though a fur is sometimes found to take the place of one or other, as in the arms of Gresley, which are: "Vairé gules and ermine." I know of no instance where vairé is found of either two metals or of two colours, nor at the same time do I know of any rule against such a combination. Probably it will be time enough to discuss the contingency when an instance comes to light. Gerard Leigh mentions vair of three or more tinctures, but instances are very rare. Parker, in his "Glossary," refers to the coat of Roger Holthouse, which he blazons: "Vairy argent, azure, gules, and or, en point."
The Vair of commerce was formerly of three sizes, and the distinction is continued in foreign armory. The middle or ordinary size is known as Vair; a smaller size as Menu-vair (whence our word "miniver"); the largest as Beffroi or Gros vair, a term which is used in armory when there are less than four rows. The word Beffroi is evidently derived from the bell-like shape of the vair, the word Beffroi being anciently used in the sense of the alarm-bell of a town. In French armory, Beffroi should consist of three horizontal rows; Vair, of four; Menu-vair, of six. This rule is not strictly observed, but in French blazon if the rows are more than four it is usual to specify the number; thus Varroux bears: de Vair de cinq traits. Menu-vair is still the blazon of some families; Banville de Trutemne bears: de Menu-vair de six tires; the Barons van Houthem bore: de Menu-vair, au franc quartier de gueules chargé de trois maillets d'or. In British armory the foregoing distinctions are unknown, and Vair is only of one size, that being at the discretion of the artist.
When the Vair is so arranged that in two horizontal rows taken together, either the points or the bases of two panes of the same tincture are in apposition, the fur is known as Counter Vair (Contre Vair) (see Fig. 39, l). Another variation, but an infrequent one, is termed Vair in Pale, known in German heraldry as Pfahlfeh (Vair appointé or Vair en pal; but if of other colours than the usual ones, Vairé en pal). In this all panes of the same colour are arranged in vertical, or palar, rows (Fig. 39, m). German heraldry apparently distinguishes between this and Stürzpfahlfeh, or reversed vair in pale. Vair in Bend (or in bend-sinister) is occasionally met with in foreign coats; thus Mignianelli in Italy bears: Vairé d'or et d'azur en bande; while Vairé en barre (that is, in bend-sinister) d'or et de sable is the coat of Pichon of Geneva.
"Vair en pointe" is a term applied by Nisbet to an arrangement by which the azure shield pointing downwards has beneath it an argent shield pointing downwards, and vice versâ, by which method the resulting effect is as shown in Fig. 39, n. The German term for this is Wogenfeh, or wave vair. Fig. 39, o, shows a purely German variety—Wechselfeh, or alternate vair; and Fig. 39, p, which is equivalent to the English vairé of four colours, is known in German armory as Buntfeh, i.e. gay-coloured or checked vair.
Ordinary vair in German heraldry is known as Eisenhüt-feh, or iron hat vair. On account of its similarity, when drawn, to the old iron hat of the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries (see Fig. 42), this skin has received the name of Eisenhutlein (little iron hat) from German heraldic students, a name which later gave rise to many incorrect interpretations. An old charter in the archives of the chapter-house of Lilienfield, in Lower Austria, under the seal (Fig. 43) of one Chimrad Pellifex, 1329, proves that at that time vair was so styled. The name of Pellifex (in German Wildwerker, a worker in skins, or furrier) is expressed in a punning or canting form on the dexter side of the shield. This Conrad the Furrier was Burgomaster of Vienna 1340-43.
A considerable number of British and foreign families bear Vair only; such are Ferrers and Gresley, above mentioned; Varano, Dukes de Camerino; Vaire and Vairière, in France; Veret, in Switzerland; Gouvis, Fresnay (Brittany); De Vera in Spain; Loheac (Brittany); Varenchon (Savoy); Soldanieri (Florence). Counter vair is borne by Loffredo of Naples; by Bouchage, Du Plessis Angers, and Brotin, of France. Hellemmes of Tournay uses: de Contre vair, à lac otice de gueules brochante sur le tout.
 Fig. 42.
|
 Fig. 43.—Seal of Chimrad Pellifex, 1329.
|
Mr. Woodward, in his "Treatise on Heraldry," writes: "Two curious forms of Vair occasionally met with in Italian or French coats are known as Plumeté and Papelonné.
In Plumeté the field is apparently covered with feathers. Plumeté d'argent et d'azur is the coat of Ceba (note that these are the tinctures of Vair); Soldonieri of Udine, Plumeté au natural (but the Soldonieri of Florence bore: Vairé argent and sable with a bordure chequy or and azure); Tenremonde of Brabant: Plumeté or and sable. In the arms of the Scaltenighi of Padua, the Benzoni of Milan, the Giolfini, Catanei, and Nuvoloni of Verona, each feather of the plumeté is said to be charged with an ermine spot sable.
The bearing of Papelonné is more frequently found; in it the field is covered with what appear to be scales, the heraldic term papelonné being derived from a supposed resemblance of these scales to the wings of butterflies; for example the coat of Monti: Gules, papelonné argent. Donzel at Besançon bears: Papelonné d'or et de sable. It is worthy of note that Donzé of Lorraine used: Gules, three bars wavy or. The Franconis of Lausanne are said to bear: de Gueules papelonné d'argent, and on a chief of the last a rose of the first, but the coat is otherwise blazoned: Vaire gules and or, &c. The coat of Arquinvilliers, or Hargenvilliers, in Picardy, of d'Hermine papelonné de gueules (not being understood, this has been blazoned "semé of caltraps"). So also the coat of Chemillé appears in French books of blazon indifferently as: d'Or papelonné de gueules: and d'Or semé de chausse-trapes de gueules. Guétteville de Guénonville is said to bear: d'Argent semé de chausse-trapes de sable, but it is more probable that this is simply d'Argent papelonné de sable. The Barisoni of Padua bear: Or, a bend of scales, bendwise argent, on each scale an ermine spot sable, the bend bordered sable. The Alberici of Bologna bear: Papelonné of seven rows, four of argent, three of or; but the Alberghi of the same city: Papelonné of six rows, three of argent, as many of gules. The connection with vairé is much clearer in the latter than in the former. Cambi (called Figliambuchi), at Florence, carried: d'Argent, papelonné de gueules; Monti of Florence and Sicily, and Ronquerolles of France the reverse.
No one who is familiar with the licence given to themselves by armorial painters and sculptors in Italy, who were often quite ignorant of the meaning of the blazons they depicted, will doubt for a moment the statement that Papelonné was originally a corruption from or perhaps is simply ill-drawn Vair."
Potent, and its less common variant Counter Potent, are usually ranked in British heraldic works as separate furs. This has arisen from the writers being ignorant that in early times Vair was frequently depicted in the form now known as Potent (see Fig. 39, q). (By many heraldic writers the ordinary Potent is styled Potent-counter-potent. When drawn in the ordinary way, Potent alone suffices.) An example of Vair in the form now known as Potent is afforded by the seal of Jeanne de Flandre, wife of Enguerrand IV. (De Courcy); here the well-known arms of Courcy, Barry of six vair and gules, are depicted as if the bars of vair were composed of bars of potent (Vrée, Généalogie des Comtes de Flandre). In a Roll of Arms of the time of Edward I. the Vair resembles Potent (-counter-potent), which Dr. Perceval erroneously terms an "invention of later date." The name and the differentiation may be, but not the fact. In the First Nobility Roll of the year 1297, the arms of No. 8, Robert de Bruis, Baron of Brecknock, are: Barry of six, Vaire ermine and gules, and azure. Here the vair is potent; so is it also in No. 19, where the coat of Ingelram de Ghisnes, or Gynes, is: Gules, a chief vair. The same coat is thus drawn in the Second Nobility Roll, 1299, No. 57. Potent, like its original Vair, is always of argent and azure, unless other tinctures are specified in the blazon. The name Potent is the old English word for a crutch or walking-staff. Chaucer, in his description of "Elde" (i.e. old age) writes:
- "So olde she was, that she ne went
- A fote, but it were by potent."
And though a potent is a heraldic charge, and a cross potent a well-known variety of that ordinary, "potent" is usually intended to indicate the fur of blue and white as in Fig. 39, q. It is not of frequent usage, but it undoubtedly has an accepted place in British armory, as also has "counter-potent," which, following the same rules as counter-vair, results in a field as Fig. 39, r. The German terms for Potent and counter-potent are respectively Sturzkrückenfeh and gegensturzkrückenfeh German heraldry has evolved yet another variant of Potent, viz. Verschobenes Gegensturzkrückenfeh (i.e. displaced potent-counter-potent), as in Fig. 39, s. There is still yet another German heraldic fur which is quite unknown in British armory. This is called Kursch, otherwise "Vair bellies," and is usually shown to be hairy and represented brown. Possibly this is the same as the Plumeté to which Mr. Woodward refers.
Some heraldic writers also speak of varry as meaning the pieces of which the vair is composed; they also use the terms vairy cuppy and vairy tassy for potent-counter-potent, perhaps from the drawings in some instances resembling cups; that is a possible meaning of tassa. It may be said that all these variations of the ancient vair arise from mere accident (generally bad drawing), supplemented by over refinement on the part of the heraldic writers who have described them. This generalisation may be extended in its application from vair to many other heraldic matters. To all intents and purposes British heraldry now or hitherto has only known vair and potent.
One of the earliest rules one learns in the study of armory is that colour cannot be placed upon colour, nor metal upon metal. Now this is a definite rule which must practically always be rigidly observed. Many writers have gone so far as to say that the only case of an infraction of this rule will be found in the arms of Jerusalem: Argent, a cross potent between four crosslets or. This was a favourite windmill at which the late Dr. Woodward tilted vigorously, and in the appendix to his "Treatise on Heraldry" he enumerates some twenty-six instances of the violation of the rule. The whole of the instances he quoted, however, are taken from Continental armory, in which these exceptions—for even on the Continent such armes fausses are noticeable exceptions—occur much more frequently than in this country. Nevertheless such exceptions do occur in British armory, and the following instances of well-known coats which break the rule may be quoted.
The arms of Lloyd of Ffos-y-Bleiddied, co. Cardigan, and Danyrallt, co. Carmarthen, are: "Sable, a spearhead imbrued proper between three scaling-ladders argent, on a chief gules a castle of the second." Burke, in his "General Armory," says this coat of arms was granted to Cadifor ap Dyfnwal, ninth in descent from Roderick the Great, Prince of Wales, by his cousin the great Lord Rhys, for taking the castle of Cardigan by escalade from the Earl of Clare and the Flemings in 1164. Another instance is a coat of Meredith recorded in Ulster's Office and now inherited by the Hon. Richard Edmund Meredith, a judge of the Supreme Court of Judicature of Ireland and a Judicial Commissioner of the Irish Land Commission. These arms are: "Gules, on a chevron sable, between three goats' heads erased, as many trefoils or." An instance of comparatively recent date will be found in the grant of the arms of Thackeray. A little careful research, no doubt, would produce a large number of English instances, but one is bound to admit the possibility that the great bulk of these cases may really be instances of augmentation.
Furs may be placed upon either metal or colour, as may also any charge which is termed proper. German heralds describe furs and natural colours as amphibious. It is perfectly legitimate to place fur upon fur, and though not often found, numbers of examples can be quoted; probably one will suffice. The arms of Richardson are: Sable, two hawks belled or, on a chief indented ermine, a pale ermines, and three lions' heads counterchanged. It is also correct to place ermine upon argent. But such coats are not very frequently found, and it is usual in designing a coat to endeavour to arrange that the fur shall be treated as metal or colour according to what may be its background. The reason for this is obvious. It is correct, though unusual, for a charge which is blazoned proper, and yet depicted in a recognised heraldic colour, to be placed upon colour; and where such cases occur, care should be taken that the charges are blazoned proper. A charge composed of more than one tincture, that is, of a metal and colour, may be placed upon a field of either; for example the well-known coat of Stewart, which is: Or, a fess chequy azure and argent; other examples being: Per pale ermine and azure, a fess wavy gules (Broadbent); and: Azure, a lion rampant argent, debruised by a fess per pale of the second and gules (Walsh); but in such coats it will usually be found that the first tincture of the composite charge should be in opposition to the field upon which it is superimposed. For instance, the arms of Stewart are: Or, a fess chequy azure and argent, and to blazon or depict them with a fess chequy argent and azure would be incorrect. When an ordinary is charged upon both metal and colour, it would be quite correct for it to be of either metal, colour, or fur, and in such cases it has never been considered either exceptional or an infraction of the rule that colour must not be placed upon colour, nor metal upon metal. There is one point, however, which is one of these little points one has to learn from actual experience, and which I believe has never yet been quoted in any handbook of heraldry, and that is, that this rule must be thrown overboard with regard to crests and supporters. I cannot call to mind an instance of colour upon colour, but a gold collar around the neck of an argent crest will constantly be met with. The sinister supporter of the Royal achievement is a case in point, and this rule, which forbids colour upon colour, and metal upon metal, only holds with regard to supporters and crests when the crest or supporter itself is treated as a field and charged with one or more objects. The Royal labels, as already stated, appear to be a standing infraction of the rule if white and argent are to be heraldically treated as identical. The rule is also disregarded entirely as regards augmentations and Scottish cadency bordures.
So long as the field is party, that is, divided into an equal number of pieces (for example, paly, barruly, or bendy, or party per bend or per chevron), it may be composed of two metals or two colours, because the pieces all being equal, and of equal number, they all are parts of the field lying in the same plane, none being charges.
Before leaving the subject of the field, one must not omit to mention certain exceptions which hardly fall within any of the before-mentioned categories. One of these can only be described by the word "landscape." It is not uncommon in British armory, though I know of but one instance where the actual field itself needs to be so described. This is the coat of the family of Franco, the paternal ancestors of Sir Massey Lopes, Bart., and Lord Ludlow. The name was changed from Franco to Lopes by Royal Licence dated the 4th of May 1831. Whether this coat of arms originated in an English grant, or whether the English grant of it amounts to no more than an attempt at the registration of a previously existing or greatly similar foreign coat of arms for the name of Franco, I am unaware, but the coat certainly is blazoned: "In a landscape field, a fountain, therefrom issuing a palm-tree all proper."
But landscape has very extensively been made use of in the augmentations which were granted at the end of the eighteenth and beginning of the nineteenth centuries. In these cases the augmentation very generally consisted of a chief and thereon a representation either of some fort or ship or action, and though the field of the augmentation is officially blazoned argent in nearly every case, there is no doubt the artist was permitted, and perhaps intended, to depict clouds and other "atmosphere" to add to the verisimilitude of the picture. These augmentations will be more especially considered in a later chapter, but here one may perhaps be permitted to remark, that execrable as we now consider such landscape heraldry, it ought not to be condemned in the wholesale manner in which it has been, because it was typical of the over elaboration to be found in all art and all artistic ideas of the period in which we find it originating. Heraldry and heraldic art have always been a mirror of the artistic ideas prevalent at equivalent periods, and unless heraldry is to be wholly relegated to consideration as a dead subject, it is an anachronism to depict an action the date of which is well known (and which date it is desired to advertise and not conceal) in a method of art belonging to a different period. In family arms the case is different, as with those the idea apparently is always the concealment of the date of nobility.
The "landscape" variety of heraldry is more common in Germany than with us, and Ströhl writes: "Of very little heraldic worth are the old house and home signs as they were used by landed proprietors, tradesmen, and artisans or workmen, as indicative of their possessions, wares, or productions. These signs, originally simply outline pictures, were later introduced into heraldic soil, inasmuch as bourgeois families raised to the nobility adopted their house signs as heraldic charges upon their shields."
There are also many coats of arms which run: "In base, a representation of water proper," and one of the best instances of this will be found in the arms of Oxford, though for the sake of preserving the pun the coat in this case is blazoned: "Argent, an ox gules passing over a ford proper." Similar instances occur in the arms of Renfrew, Queensferry, Leith, Ryde, and scores of other towns. It has always been considered permissible to represent these either by an attempt to depict natural water, or else in the ancient heraldic way of representing water, namely "barry wavy argent and azure." There are many other coats of arms which are of a similar character though specifically blazoned "barry wavy argent and azure." Now this representation of water in base can hardly be properly said to be a charge, but perhaps it might be dismissed as such were it not that one coat of arms exists in Scotland, the whole of the field of which is simply a representation of water. Unfortunately this coat of arms has never been matriculated in Lyon Register or received official sanction; but there is no doubt of its ancient usage, and were it to be now matriculated in conformity with the Act of 1672, there is very little doubt that the ancient characteristic would be retained. The arms are those of the town of Inveraray in Argyllshire, and the blazon of the coat, according to the form it is depicted upon the Corporate seal, would be for the field: "The sea proper, therein a net suspended from the dexter chief and the sinister fess points to the base; and entangled in its meshes five herrings," which is about the most remarkable coat of arms I have ever come across.
Occasionally a "field," or portion of a field, will be found to be a representation of masonry. This may be either proper or of some metal or colour. The arms of the city of Bath are: "Party per fesse embattled azure and argent, the base masonry, in chief two bars wavy of the second; over all, a sword in pale gules, hilt and pommel or." The arms of Reynell are: "Argent, masoned sable, a chief indented of the second."
SEME
The use of the term "semé" must be considered before we leave the subject of the field. It simply means "powdered with" or "strewed with" any objects, the number of the latter being unlimited, the purpose being to evenly distribute them over the shield. In depicting anything semé, care is usually taken that some of the charges (with which the field is semé) shall be partly defaced by the edges of the shield, or the ordinary upon which they are charged, or by the superior charge itself, to indicate that the field is not charged with a specific number of objects.
There are certain special terms which may be noted. A field or charge semé of fleurs-de-lis is termed "semé-de-lis," but if semé of bezants it is bezanté, and is termed platé if semé of plates.
A field semé of billets is billetty or billetté, and when semé of cross crosslets it is termed crusilly. A field or charge semé of drops is termed goutté or gutty.
Instances of coats of which the field is semé will be found in the arms of De la Warr (see Fig. 44), which are: Gules, crusilly, and a lion rampant argent; Beaumont (see Fig. 45): Azure, semé-de-lis and a lion rampant or; and Umfraville (see Fig. 46): Gules, semé of crosses flory, and a cinquefoil or.
The goutte or drop occasionally figures (in a specified number) as a charge; but such cases are rare, its more frequent use being to show a field semé. British heraldry alone has evolved separate names for the different colours, all other nations simply using the term "goutté" or "gutté," and specifying the colour. The terms we have adopted are as follows: For drops of gold, "gutté-d'or"; silver, "gutté-d'eau"; for gules, "gutté-de-sang"; azure, "gutté-de-larmes"; vert, "gutté-d'huile"; and sable, "gutté-de-poix."
The term semé must not be confused with diapering, for whilst the objects with which a field is semé are an integral part of the arms, diapering is a purely artistic and optional matter.
DIAPERING
The diapering of armorial emblazonments is a matter with which the Science of armory has no concern. Diaper never forms any part of the blazon, and is never officially noticed, being considered, and very properly allowed to remain, a purely artistic detail. From the artistic point of view it has some importance, as in many of the earliest instances of handicraft in which armorial decoration appears, very elaborate diapering is introduced. The frequency with which diapering is met with in armorial handicraft is strangely at variance with its absence in heraldic paintings of the same periods, a point which may perhaps be urged upon the attention of some of the heraldic artists of the present day, who would rather seem to have failed to grasp the true purpose and origin and perhaps also the use of diaper. In stained glass and enamel work, where the use of diaper is most frequently met with, it was introduced for the express purpose of catching and breaking up the light, the result of which was to give an enormously increased effect of brilliance to the large and otherwise flat surfaces. These tricks of their art and craft the old handicraftsmen were past masters in the use of. But no such purpose could be served in a small painting upon vellum. For this reason early heraldic emblazonments are seldom if ever found to have been diapered. With the rise of heraldic engraving amongst the "little masters" of German art, the opportunity left to their hands by the absence of colour naturally led to the renewed use of diaper to avoid the appearance of blanks in their work. The use of diaper at the present day needs to be the result of careful study and thought, and its haphazard employment is not recommended.
If, as Woodward states (an assertion one is rather inclined to doubt), there are some cases abroad in which the constant use of diapering has been stereotyped into an integral part of the arms, these cases must be exceedingly few in number, and they certainly have no counterpart in the armory of this country. Where for artistic reasons diapering is employed, care must always be taken that the decorative form employed cannot be mistaken for a field either charged or semé.
PARTITION LINES
If there is one subject which the ordinary text-books of armory treat in the manner of classification adapted to an essay on natural history or grammar, with its attendant rigidity of rule, it is the subject of partition lines; and yet the whole subject is more in the nature of a set of explanations which must each be learned on its own merits. The usual lines of partition are themselves well enough known; and it is hardly necessary to elaborate the different variations at any great length. They may, however, be enumerated as follows: Engrailed, embattled, indented, invecked or invected, wavy or undy, nebuly, dancetté, raguly, potenté, dovetailed, and urdy. These are the lines which are recognised by most modern heraldic text-books and generally recapitulated; but we shall have occasion later to refer to others which are very well known, though apparently they have never been included in the classification of partition lines (Fig. 47). Engrailed, as every one knows, is formed by a continuous and concurrent series of small semicircles conjoined each to each, the sharp points formed by the conjunction of the two arcs being placed outwards. This partition line may be employed for the rectilinear charges known as "ordinaries" or "sub-ordinaries." In the bend, pale, pile, cross, chief, and fess, when these are described as engrailed the enclosing lines of the ordinary, other than the edges of the shield, are all composed of these small semicircles with the points turned outwards, and the word "outwards" must be construed as pointing away from the centre of the ordinary when it is depicted. In the case of a chief the points are turned downwards, but it is rather difficult to describe the use of the term when used as a partition line of the field. The only instance I can call to mind where it is so employed is the case of Baird of Ury, the arms of this family being: Per pale engrailed gules and or, a boar passant counterchanged. In this instance the points are turned towards the sinister side of the shield, which would seem to be correct, as, there being no ordinary, they must be outwards from the most important position affected, which in this case undoubtedly is the dexter side of the shield. In the same way "per fess engrailed" would be presumably depicted with the points outwards from the chief line of the shield, that is, they would point downwards; and I should imagine that in "per bend engrailed" the points of the semicircles would again be placed inclined towards the dexter base of the shield, but I may be wrong in these two latter cases, for they are only supposition. This point, however, which puzzled me much in depicting the arms of Baird of Ury, I could find explained in no text-book upon the subject.

Fig. 47.—Lines of Partition.
The term invected or invecked is the precise opposite of engrailed. It is similarly composed of small semicircles, but the points are turned inwards instead of outwards, so that it is no more than the exact reverse of engrailed, and all the regulations concerning the one need to be observed concerning the other, with the proviso that they are reversed.
The partition line embattled has certain peculiarities of its own. When dividing the field there can be no difficulty about it, inasmuch as the crenellations are equally inwards and outwards from any point, and it should be noted that the term "crenellé" is almost as often used as "embattled." When, however, the term describes an ordinary, certain points have to be borne in mind. The fess or the bar embattled is drawn with the crenellations on the upper side only, the under edge being plain unless the ordinary is described both as "embattled and counter-embattled." Similarly a chevron is only crenellated on the upper edge unless it is described as both embattled and counter-embattled, but a pale embattled is crenellated on both edges as is the cross or saltire. Strictly speaking, a bend embattled is crenellated upon the upper edge only, though with regard to this ordinary there is much laxity of practice. I have never come across a pile embattled; but it would naturally be embattled on both edges. Some writers make a distinction between embattled and bretessed, giving to the former term the meaning that the embattlements on the one side are opposed to the indentations on the other, and using the term bretessed to signify that embattlements are opposite embattlements and indentations opposite indentations. I am doubtful as to the accuracy of this distinction, because the French term bretessé means only counter-embattled.
The terms indented and dancetté need to be considered together, because they differ very little, and only in the fact that whilst indented may be drawn with any number of teeth, dancetté is drawn with a limited number, which is usually three complete teeth in the width of the field. But it should be observed that this rule is not so hard and fast that the necessity of artistic depicting may not modify it slightly. An ordinary which is indented would follow much the same rules as an ordinary which was engrailed, except that the teeth are made by small straight lines for the indentations instead of by small semicircles, and instances can doubtless be found of all the ordinaries qualified by the term indented. Dancetté, however, does not lend itself so readily to general application, and is usually to be found applied to either a fess or chief, or occasionally a bend. In the case of a fess dancetté the indentations on the top and bottom lines are made to fit into each other, so that instead of having a straight band with the edge merely toothed, one gets an up and down zig-zag band with three complete teeth at the top and three complete teeth at the bottom. Whilst a fess, a bar, a bend, and a chief can be found dancetté, I do not see how it would be possible to draw a saltire or a cross dancetté. At any rate the resulting figure would be most ugly, and would appear ill-balanced. A pile and a chevron seem equally impossible, though there does not seem to be the like objection to a pale dancetté. An instance of a bend dancetté is found in the arms of Cuffe (Lord Desart), which are: Argent, on a bend dancetté sable, plain cotised azure, three fleurs-de-lis, and on each cotise as many bezants.
Wavy or undy, which is supposed to have been taken from water, and nebuly, which is supposed to be derived from clouds, are of course lines which are well known. They are equally applicable to any ordinary and to any partition of the field; but in both cases it should be noticed by artists that there is no one definite or accepted method of depicting these lines, and one is quite at liberty, and might be recommended, to widen out the indentations, or to increase them in height, as the artistic requirements of the work in hand may seem to render advisable. It is only by bearing this in mind and treating these lines with freedom that really artistic work can sometimes be produced where they occur. There is no fixed rule either as to the width which these lines may occupy or as to the number of indentations as compared with the width of the shield, and it is a pity to introduce or recognise any regulations of this character where none exist. There are writers who think it not unlikely that vairé and barry nebuly were one and the same thing. It is at any rate difficult in some old representations to draw any noticeable distinctions between the methods of depicting barry nebuly and vair.
The line raguly has been the subject of much discussion. It, and the two which follow, viz. potenté and dovetailed, are all comparatively modern introductions. It would be interesting if some enthusiast would go carefully through the ancient Rolls of Arms and find the earliest occurrences of these terms. My own impression is that they would all be found to be inventions of the mediæval writers on heraldry. Raguly is the same as embattled, with the crenellations put upon the slant. Some writers say they should slant one way, others give them slanting the reverse. In a pale or a bend the teeth must point upwards; but in a fess I should hesitate to say whether it were more correct for them to point to the dexter or to the sinister, and I am inclined to consider that either is perfectly correct. At any rate, whilst they are usually drawn inclined to the dexter, in Woodward and Burnett they are to the sinister, and Guillim gives them turned to the dexter, saying, "This form of line I never yet met with in use as a partition, though frequently in composing of ordinaries referring them like to the trunks of trees with the branches lopped off, and that (as I take it) it was intended to represent." Modern heraldry supplies an instance which in the days of Mr. Guillim, of course, did not exist to refer to. This instance occurs in the arms of the late Lord Leighton, which were: "Quarterly per fesse raguly or and gules, in the second and third quarters a wyvern of the first." It is curious that Guillim, even in the edition of 1724, does not mention any of the remaining terms. Dovetailed in modern armory is even yet but seldom made use of, though I can quote two instances of coats of arms in which it is to be found, namely, the arms of Kirk, which are: "Gules, a chevron dovetailed ermine, on a chief argent, three dragons' heads couped of the field;" and Ambrose: "Azure, two lions passant in pale argent, on a chief dovetailed of the last, a fleur-de-lis between two annulets of the first." Other instances of dovetailed used as a line of partition will be found in the case of the arms of Farmer, which are: "Per chevron dovetailed gules and argent, in chief two lions' heads erased of the last, and in base a salamander in flames proper;" and in the arms of Fenton namely: "Per pale argent and sable, a cross dovetailed, in the first and fourth quarters a fleur-de-lis, and in the second and third a trefoil slipped all countercharged." There are, of course, many others. The term potenté, as will be seen from a reference to Fig. 47, is used to indicate a line which follows the form of the division lines in the fur potent. As one of the partition lines potenté is very rare.
As to the term urdy, which is given in Woodward and Burnett and also in Berry, I can only say I personally have never come across an instance of its use as a partition line. A cross or a billet urdy one knows, but urdy as a partition line I have yet to find. It is significant that it is omitted in Parker except as a term applicable to a cross, and the instances and variations given by Berry, "urdy in point paleways" and "contrary urdy," I should be much more inclined to consider as variations of vair; and, though it is always well to settle points which can be settled, I think urdy and its use as a partition line may be well left for further consideration when examples of it come to hand.
There is one term, however, which is to be met with at the present time, but which I have never seen quoted in any text-book under the heading of a partition line; that is, "flory counter-flory," which is of course formed by a succession of fleurs-de-lis alternately reversed and counterchanged. They might of course be blazoned after the quotation of the field as "per bend" or "per chevron" as the case might be, simply as so many fleurs-de-lis counterchanged, and alternately reversed in a specified position; but this never appears to be the case, and consequently the fleurs-de-lis would appear to be essentially parts of the field and not charges. I have sometimes thought whether it would not be more correct to depict "per something" flory and counter-flory without completing the fleurs-de-lis, simply leaving the alternate tops of the fleurs-de-lis to show. In the cases of the illustrations which have come under my notice, however, the whole fleur-de-lis is depicted, and as an instance of the use of the term may be mentioned the arms of Dumas, which are: "Per chevron flory and counter-flory or and azure, in chief two lions' gambs erased, and in base a garb counterchanged." But when the term flory and counter-flory is used in conjunction with an ordinary, e.g. a fess flory and counter-flory, the half fleurs-de-lis, only alternately reversed, are represented on the outer edges of the ordinary.
I think also that the word "arched" should now be included as a partition line. I confess that the only form in which I know of it is that it is frequently used by the present Garter King of Arms in designing coats of arms with chiefs arched. Recently Garter has granted a coat with a chief double arched. But if a chief can be arched I see no reason why a fesse or a bar cannot equally be so altered, and in that case it undoubtedly becomes a recognised line of partition. Perhaps it should be stated that a chief arched is a chief with its base line one arc of a large circle. The diameter of the circle and the consequent acuteness of the arch do not appear to be fixed by any definite rule, and here again artistic requirements must be the controlling factor in any decision. Elvin in his "Dictionary of Heraldic Terms" gives a curious assortment of lines, the most curious of all, perhaps, being indented embowed, or hacked and hewed. Where such a term originated or in what coat of arms it is to be found I am ignorant, but the appearance is exactly what would be presented by a piece of wood hacked with an axe at regular intervals. Elvin again makes a difference between bretessed and embattled-counter-embattled, making the embattlement on either side of an ordinary identical in the former and alternated in the latter. He also makes a difference between raguly, which is the conventional form universally adopted, and raguled and trunked, where the ordinary takes the representation of the trunk of a tree with the branches lopped; but these and many others that he gives are refinements of idea which personally I should never expect to find in actual use, and of the instances of which I am unaware. I think, however, the term "rayonné," which is found in both the arms of O'Hara and the arms of Colman, and which is formed by the addition of rays to the ordinary, should take a place amongst lines of partition, though I admit I know of no instance in which it is employed to divide the field.
METHODS OF PARTITION
The field of any coat of arms is the surface colour of the shield, and is supposed to include the area within the limits formed by its outline. There are, as has been already stated, but few coats of a single colour minus a charge to be found in British heraldry. But there are many which consist of a field divided by partition lines only, of which some instances were given on page 69.
A shield may be divided by partition lines running in the direction of almost any "ordinary," in which case the field will be described as "per bend" or "per chevron," &c. It may be:
| Per fess | Fig. | 48 |
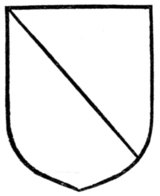
| Per bend | " | 49 |
| Per bend sinister | " | 50 |
| Per pale | " | 51 |
| Per chevron | " | 52 |
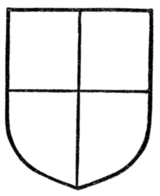
| Per cross | " | 53 |
| (though it should be noted that the more usual term employed for this is "quarterly") | ||
| Per saltire | Fig. | 54 |
But a field cannot be "per pile" or "per chief," because there is no other way of representing these ordinaries.
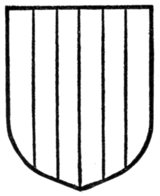
A field can be composed of any number of pieces in the form of the ordinaries filling the area of the shield, in which case the field is said to be "barry" (Figs. 55 and 56), "paly" (Fig. 57), "bendy" (Fig. 58), "chevronny" (Fig. 59), &c., but the number of pieces must be specified.
Another method of partition will be found in the fields "checky" (or "chequy") and lozengy; but these divisions, as also the foregoing, will be treated more specifically under the different ordinaries. A field
which is party need not necessarily have all its lines of partition the same. This peculiarity, however, seldom occurs except in the case of a field quarterly, the object in coats of this character being to prevent different quarters of one coat of arms being ranked as or taken to be quarterings representing different families.
- ↑ The arms of Clayhills of Invergowrie: Parted per bend sanguine and vert, two greyhounds courant bendwise argent. Mantling gules doubled argent; and upon a wreath of the liveries is set for crest, an arm holding an Imperial crown proper; and in an escroll over the same, this motto, "Corde et animo." Matriculated in Lyon Office circa 1672.