is celebrated there six times a year. On the north of and adjoining the old church stands the new cathedral, built from designs by Juan Gil de Ontanon. Though begun in 1509 the work of construction made little progress until 1513, when it was entrusted to Ontañon under Bishop Francisco de Bobadilla; though not finished till 1734, it is a notable example of the late Gothic and Plateresque styles. Its length is 340 ft. and its breadth 160 ft. The interior is fairly Gothic in character, but on the outside the Renaissance spirit shows itself more clearly, and is fully developed in the dome. Everywhere the attempt at mere novelty or richness results in feebleness. The main arch of the great portal consists of a simple trefoil, but the label above takes an ogee line, and the inner arches are elliptical. Above the doors are bas-reliefs, foliage, &c., which in exuberance of design and quality of workmanship are good examples of the latest efforts of Spanish Gothic. The church contains paintings by J. F. de Navarrete (1526–1579) and L. de Morales (c. 1509–1586), and some overrated statues by Juan de Juni (16th century). The treasury is very rich, and amongst other articles possesses a custodia which is a masterpiece of goldsmith's work, and a bronze crucifix of undoubted authenticity, which was borne before the Cid in battle. The great bell weighs over 23 tons. Of the university buildings the façade of the library is a peculiarly rich example of late 15th-century Gothic. The cloisters are light and elegant; the grand staircase ascending from them has a fine balustrade of foliage and figures. The Colegio de Nobles Irlandeses, formerly Colegio de Santiago Apostol, was built in 1521 from designs by Pedro de Ibarra. The double arcaded cloister is a fine piece of work of the best period of the Renaissance. The jesuit College is an immense and ugly Renaissance building begun in 1614 by Juan Gomez de Mora. The Colegio Viejo, also called San Bartolomé, was rebuilt in the 18th century, and now serves as the overnor's palace. The convent of Santo Domingo, sometimes called San Esteban, shows a mixture of styles from the 13th century onwards. The church is Gothic with a Plateresque façade of great lightness and delicacy. It is of purer design than that of the cathedral; nevertheless it shows the tendency of the period. The reredos, one of the finest Renaissance works in Spain, contains statues by Salvador Carmona, and a curious bronze statuette of the Virgin and Child on a throne of champlevé enamel of the 12th century. The chapter-house, built by Juan Moreno in 1637, and the staircase and sacristy are good examples of later work. The convent of the Augustinas Recoletas, begun by Fontana in 1616, is in better taste than any other Renaissance building in the city. The church is rich in marble fittings and contains several fine pictures of the Neapolitan school, especially the Conception by J. Ribera (1588–1656) over the altar. The convent of the Espirita Santo has a good door by A. Berruguete (c. 1480–1561). There is also a rather effective portal to the convent of Las Dueñas. The church of S. Marcos is a curious circular building with three eastern apses; and the churches of S. Martin and S. Matteo have good earl doorways. Many of the private houses are untouched examples of the domestic architecture of the prosperous times in which they were built. Such are the Casa de las Conchas, the finest example of its period in Spain; the Casa de la Sal, with a magnificent courtyard and sculptured gallery; and the palaces of Maldonado, Monterey and Espinosa.
In the middle ages the trade of Salamanca was not insignificant, and the stamped leather-work produced there is still sought after. Its manufactures are now of little consequence, and consist of china, cloth and leather. The transport trade is, however, of more importance, and shows signs of increasing, as a result of the extension of railway communication between 1875 and 1900. During this period the population increased by nearly 7000.
History.—The town was of importance as early as 222 B.C., when it was captured by Hannibal from the Vettones; and it afterwards became under the Romans the ninth station on the Via Lata from Merida to Saragossa. It passed successively under the rule of the Goths and the Moors, till the latter were finally driven out about 1055. About 1100 many foreign settlers were induced by Alphonso VI. to establish themselves in the district, and the city was enlarged and adorned by Count Raymond of Burgundy and his wife, the Princess Urraca. The Fuero de Salamanca, a celebrated code of civil law, probably dates from about 1200. Thenceforward, until the second half of the 16th century, the prosperity of the university rendered the city one of the most important in Spain. But in 1593 the establishment of an independent bishopric at Valladolid (then the seat of the court), which had previously been subject to the see of Salamanca, dealt a serious blow to the prestige of the city; and its commerce was shattered by the expulsion of the Moriscos in 1610 and the wars of the 18th and 19th centuries.
See Villar y Macias, Historia de Salamanca (3 vols., Salamanca, 1887); H. Rashdall, Universities of Europe in the Middle Ages, vol. ii. pt. I. (London, 1895); Lapunya, La Universidad de Salamanca y la cultura española en el siglo XIII. (Paris, 1900). (K. G. J.)
Battle of Salamanca, 1812. (For the operations which preceded this battle see Peninsular War.) On the 22nd of July 1812 the Allied army under Wellington (about 46,000 with 60 guns) was drawn up south of Salamanca, the left resting on the river Tormes at Santa Marta, with a division under Pakenham and some cavalry on the north bank at Cabrerizos; the right near the village of Arapiles and two hills of that name. Wellington's object was to cover Salamanca and guard his communications through Ciudad Rodrigo with Portugal. The French under Marshal Marmont (about 42,000 with 70 guns) were collecting towards Wellington's right, stretching southwards from Calvariza de Ariba. The country generally is undulating, but crossed by some marked ridges and streams.
Until the morning of the battle it had been uncertain whether Marmont wished to reach Salamanca by the right or left bank of the Tormes, or to gain the Ciudad Rodrigo road, but Wellington now felt that the latter was his real objective. At daylight there was a rush by both armies for the two commanding hills of the Arapiles; the Allies gained the northern (since termed the "English"), and the French the southern (since termed the "French") Arapiles. While Marmont was closing up his forces, a complete change of position was carried out by Wellington. Pakenham was directed to march through Salamanca, crossing the Tormes, and move under cover to a wood near Aldea Tejada, while Wellington, holding the village of Arapiles and the northern hill, took up a line with four infantry divisions, a Portuguese brigade (Bradford), a strong force of cavalry, and Don Carlos's Spanish brigade, under cover of a ridge between Arapiles and Aldea Tejada. By noon his old right had become his left, and he was nearer to the Ciudad Rodrigo road, flanking Marmont should he move towards it.
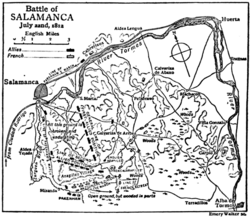
Redrawn from Maj.-Gen. C. W. Robinson's Wellington's Campaigns, by permission of Hugh Rees, Ltd.
It was not Wellington's wish (Despatches, July 21, 1812) to light a battle "unless under very advantageous circumstances." He knew that large reinforcements were nearing the French, and, having determined to fall back towards Portugal, he began to pass his baggage along the Ciudad Rodrigo road. Marmont, about 2 p.m., seeing the dust of his baggage column, ignorant of his true position, and anxious to intercept his retreat, ordered two divisions under Maucune, the leading one of which became afterwards Thomiéres',[1] to push westward, while he himself attacked Arapiles. Maucune moved off, flanked by some cavalry and fifty guns, leaving a gap between him and the rest of the French. Wellington instantly took advantage of this. Directing Pakenham to attack the head of the leading French division, and a Portuguese brigade (Pack) to occupy the enemy by assaulting the south (or French) Arapiles, he prepared to 'bear down in strength upon Maucune's right flank. The French attack upon Arapiles was after hard fighting repulsed; and, at about 5 p.m., Maucune's force, when in confusion from the fierce attack of Pakenham and Wellington in front and flank and suffering severely, was suddenly trampled down "with a terrible clamour and disturbance" (Napier) by an irresistible charge of Le Marchant's and Anson's cavalry under Sir Stapleton Cotton. This counter stroke decided the battle, Marmont's left wing being completely broken. The French made a gallant but fruitless effort to retrieve the day, and repulsed Pack's attack upon the French Arapiles; but, as the light waned, Clausel, Marmont being Wounded, drew off the French army towards Alba de Tormes' and retired to Valladolid. Both armies lost heavily, the Allies about 6000, the French some 15,000 men, 12 guns 2 eagles and several standards. The rout would have been even more thorough had not the castle and ford at Alba de
- ↑ Some authorities differ as to this (see The Salamanca Campaii by Captain A. H. Marindin, 1906, appendix, pp. 51-59).

