overlordship. The political history of Mantineia begins soon after the Persian wars, when its five constituent villages, at the suggestion of Argos, were merged into one city, whose military strength forthwith secured it a leading position in the Peloponnesus. Its policy was henceforth guided by three main considerations. Its democratic constitution, which seems to have been entirely congenial to the population of small freeholders, and its ambition to gain control over the Alpheus watershed and both the Arcadian high roads to the isthmus, frequently estranged Mantineia from Sparta and threw it into the arms of Argos. But the chronic frontier disputes with Tegea, which turned the two cities into bitter enemies, contributed most of all to determine their several policies. About 469 B.C. Mantineia alone of Arcadian townships refused to join the league of Tegea and Argos against Sparta. Though formally enrolled on the same side during the Peloponnesian War the two cities used the truce of 423 to wage a fierce but indecisive war with each other. In the time following the peace of Nicias the Mantineians, whose attempts at expansion beyond Mount Maenalus were being foiled by Sparta, formed a powerful alliance with Argos, Elis and Athens (420), which the Spartans, assisted by Tegea, broke up after a pitched battle in the city’s territory (418). In the subsequent years Mantineia still found opportunity to give the Athenians covert help, and during the Corinthian War (394–387) scarcely disguised its sympathy with the anti-Spartan league. In 385 the Spartans seized a pretext to besiege and dismantle Mantineia and to scatter its inhabitants among four villages. The city was reconstituted after the battle of Leuctra and under its statesman Lycomedes played a prominent part in organizing the Arcadian League (370). But the long-standing jealousy against Tegea, and a recent one against the new foundation of Megalopolis, created dissensions which resulted in Mantineia passing over to the Spartan side. In the following campaign of 362 Mantineia, after narrowly escaping capture by the Theban general Epaminondas, became the scene of a decisive conflict in which the latter achieved a notable victory but lost his own life. After the withdrawal of the Thebans from Arcadia Mantineia failed to recover its pre-eminence from Megalopolis, with which city it had frequent disputes. In contrast with the Macedonian sympathies of Megalopolis Mantineia joined the leagues against Antipater (322) and Antigonus Gonatas (266). A change of constitution, imposed perhaps by the Macedonians, was nullified (about 250) by a revolution through which democracy was restored. About 235 B.C. Mantineia entered the Achaean League, from which it had obtained protection against Spartan encroachments, but soon passed in turn to the Aetolians and to Cleomenes III. of Sparta. A renewed defection, inspired apparently by aversion to the aristocratic government of the Achaeans and jealousy of Megalopolis, was punished in 222 by a thorough devastation of the city, which was now reconstituted as a dependency of Argos and renamed Antigoneia in honour of the Achaeans’ ally Antigonus Doson. Mantineia regained its autonomous position in the Achaean League in 192, and its original name during a visit of the emperor Hadrian in A.D. 133. Under the later Roman Empire the city dwindled into a mere village, which since the 6th century bore the Slavonic name of Goritza. It finally became a prey to the malaria which arose when the plain fell out of cultivation, and under Turkish rule disappeared altogether. (M. O. B. C.)

|
| Walker & Cockerell sc. |
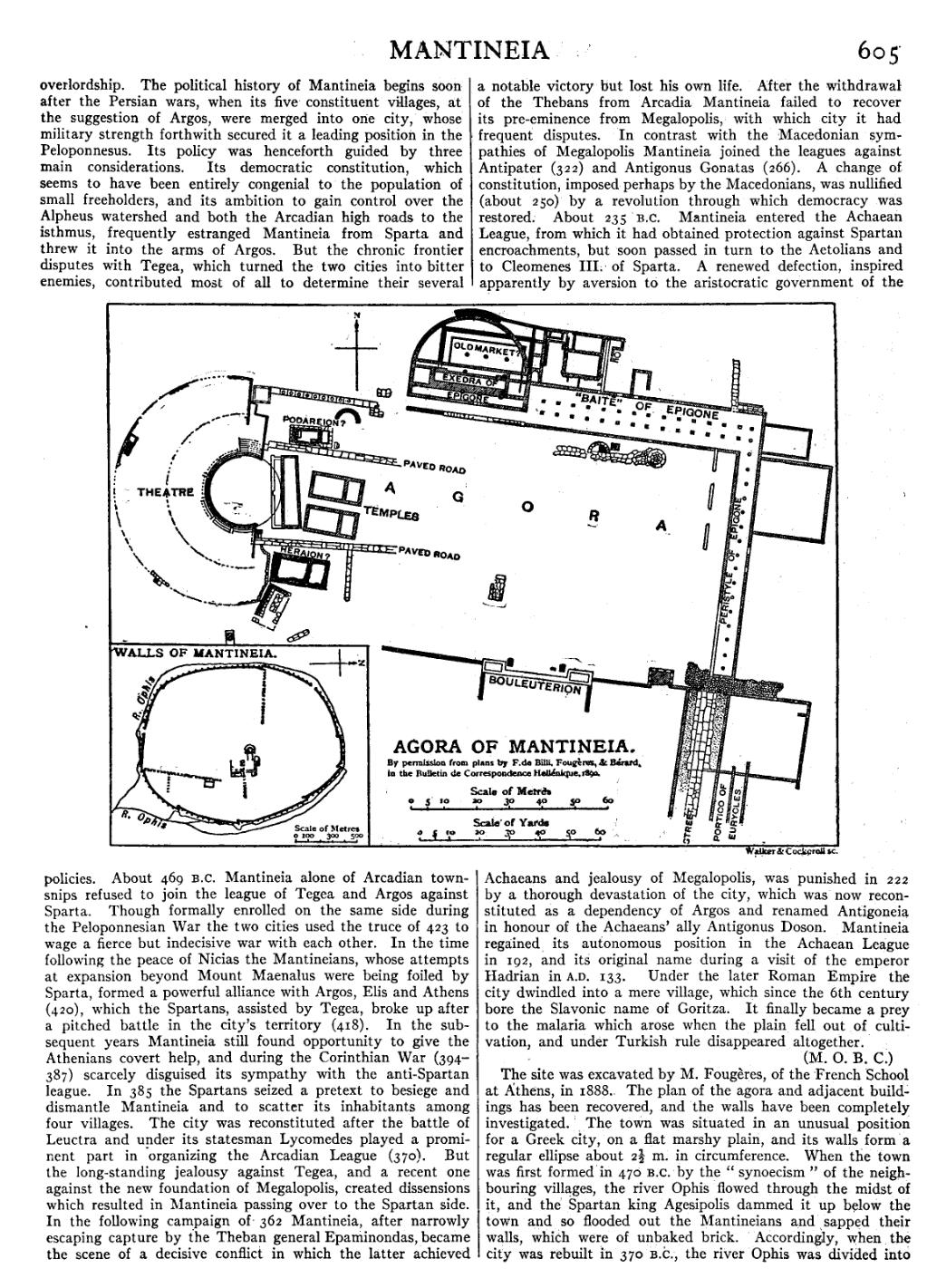
The site was excavated by M. Fougères, of the French School at Athens, in 1888. The plan of the agora and adjacent buildings has been recovered, and the walls have been completely investigated. The town was situated in an unusual position for a Greek city, on a flat marshy plain, and its walls form a regular ellipse about 212 m. in circumference. When the town was first formed in 470 B.C. by the “synoecism” of the neighbouring villages, the river Ophis flowed through the midst of it, and the Spartan king Agesipolis dammed it up below the town and so flooded out the Mantineians and sapped their walls, which were of unbaked brick. Accordingly, when the city was rebuilt in 370 B.C., the river Ophis was divided into